FINDING SUBSTITUTE SURFACTANTS FOR SYNPERONIC N
JOHN A. FIELDS, ANDREW WINGHAM, FRANCES HARTOG, & VINCENT DANIELS
10 CONCLUSIONS FROM PHASE 2
The results for color change allowed several factors to be highlighted. The variation in color measurements for wool was minimal. It was apparent from the readings how easily and rapidly woolen fabrics can discolor. The variation between the cotton results was in all cases within the bounds of error, and thus they were discounted.
The tensile testing results illustrated variations between aged and unaged samples in the case of both cotton and woolen fabrics. The results yielded very limited information with which to distinguish between the individual surfactants and their effects on the strength reduction. It was clear that no individual
Table .
Change in pH and Δ Values of Unsoiled Cotton Textiles from Prewashing to Postwashing and Aging (where performed)
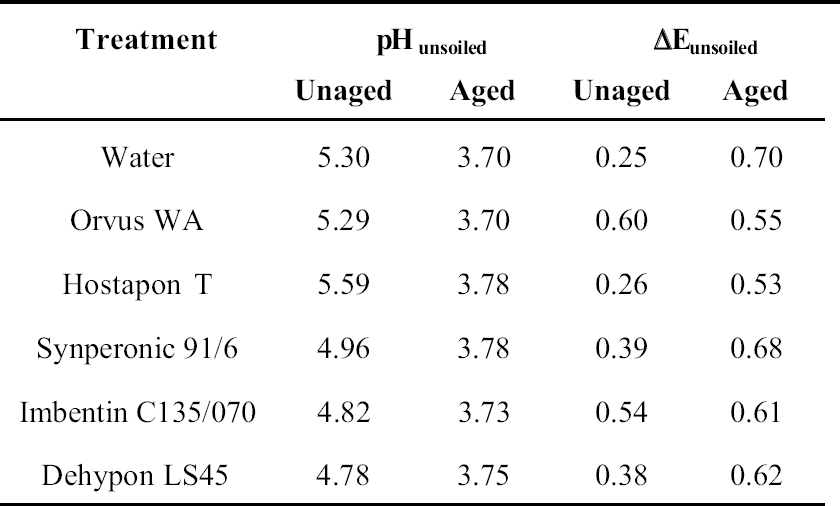 |
Table .
Change in pH and Δ Values of Unsoiled Wool Textiles from Prewashing to Postwashing and Aging (where performed)
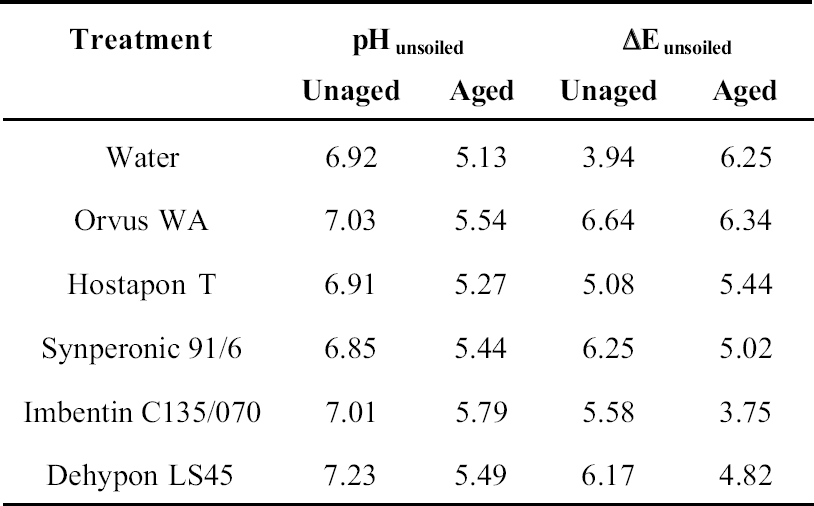 |
Fig. 8.
Mean maximum load values for cotton samples (� standard deviation)
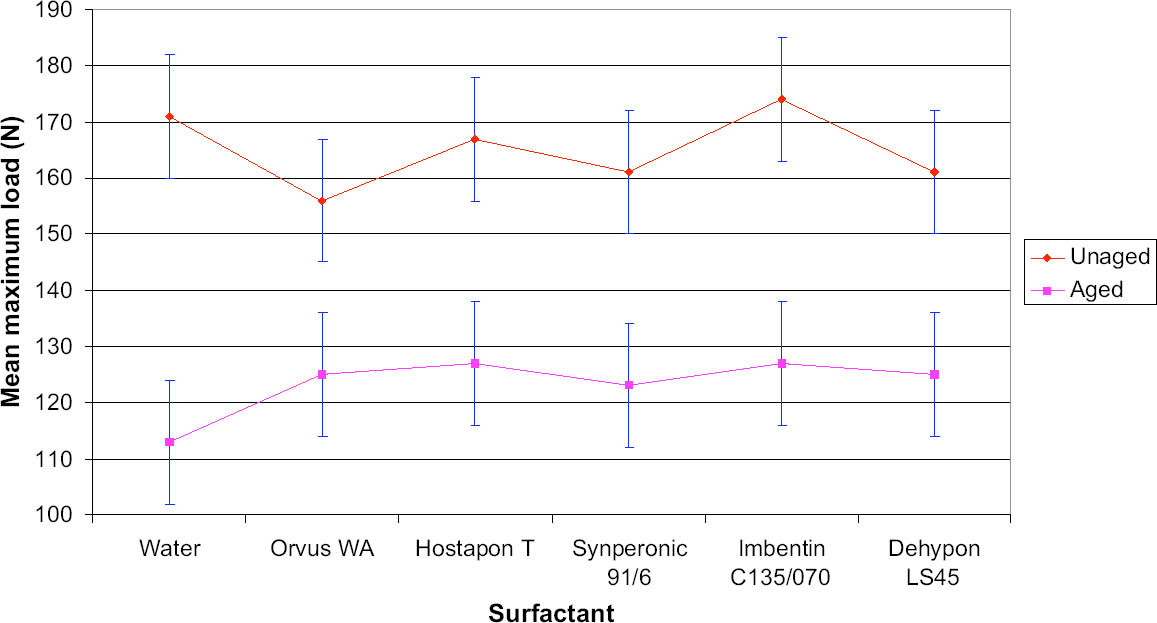 |
Fig. 9.
Mean maximum load values for wool samples (� standard deviation)
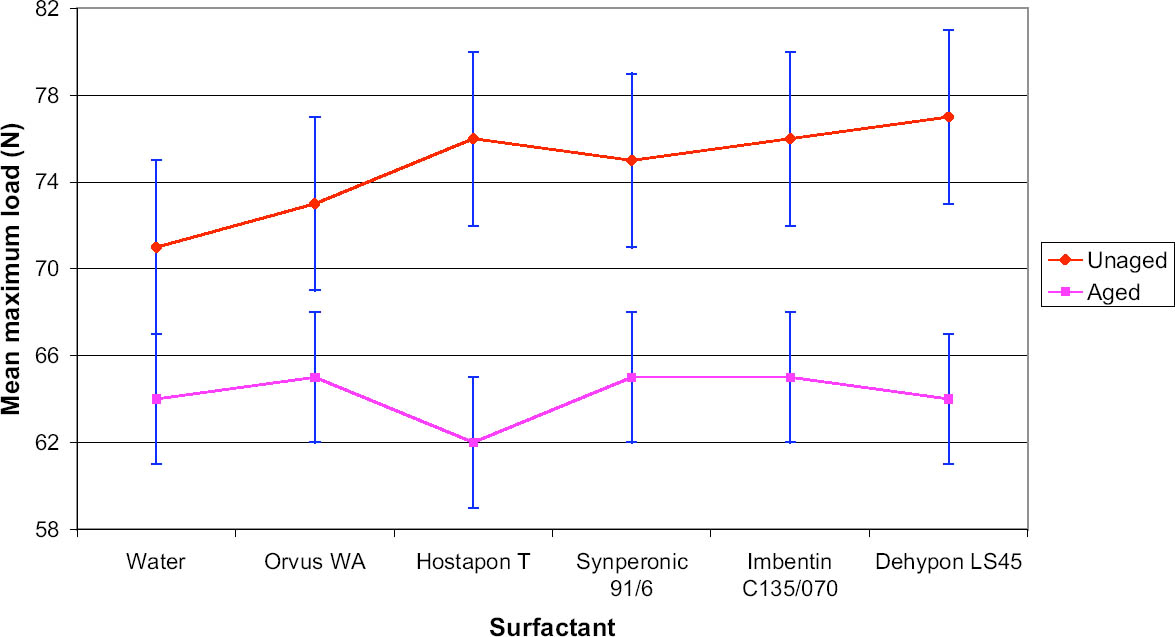 |
surfactant caused appreciable loss of strength to the fabric.
|