PENETRATION AND PLACEMENT OF ALKALINE COMPOUNDS IN SOLUTION-DEACIDIFIED PAPER
George B. Kelly, & Stanley Fowler
REFERENCES
Chemist, Research and Testing Laboratory, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C.
Physical Science Technician, Research and Testing Laboratory, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C.
Barrow, W. J. (1963–64), “Permanence/Durability of the Book,” Richmond, Virginia, The Dietz Press, Inc., I–III.
W. M.Best, “The Principles of the Law of Evidence,” American Edition, Soule & Bugbee, 1883. pH of paper = 4.5, thickness − 0.0042″, Gurley Porosity = 42 secs/100ml, acidity = 56mEq/Kg.
Alkali Determination in Paper: Weigh a 1 to 2.5g sample of paper to the nearest 0.001g and disperse in 200ml of distilled water in a Waring Blendor. Transfer to a 400ml beaker using about 50ml of distilled water to transfer any fibrous residues from the blender. Measure the pH with a pH meter and add sufficient 0.1 N hydrochloric acid (HCI) to reduce the pH to less than 3.0. Add exactly the same volume of 0.1N HCI to 250ml of distilled water in another beaker as a blank. Heat both beakers until the solutions boil, and boil gently for 1 minute to expel carbon dioxide. Cool to room temperature and back-titrate each to a pH of 7.0 with 0.1000N sodium hydroxide solution (pH meter). Calculate the alkali present as follows:
Fig. .
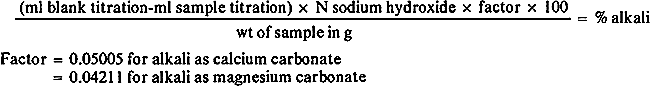 |
J. C.Williams, et. al., U. S. Patent 3898356 (1975).
Caution: Oven drying is only a possibility to be considered. It may be detrimental, particularly with art works or manuscripts.
|